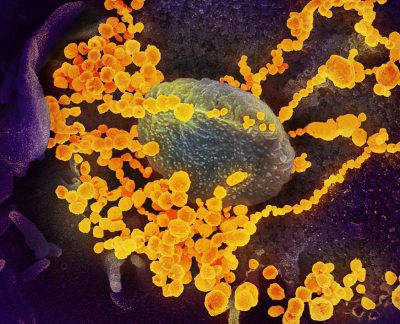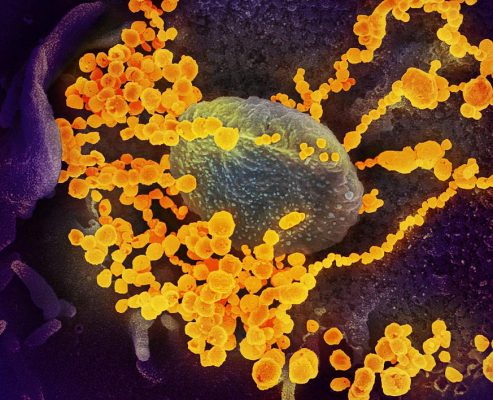
Electron microscope image shows SARS-CoV-2, also known as 2019-nCoV (round gold objects) emerging from the surface of cells cultured in the lab
Study supports clinical testing under way across U.S.
April 17, 2020 – Scientists at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), a part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), reported today that early treatment with the experimental antiviral drug remdesivir, developed by Gilead Sciences of Foster City, California, significantly reduced clinical disease and damage to the lungs of rhesus macaques infected with SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus that causes COVID-19.
The study was designed to follow dosing and treatment procedures used for hospitalized COVID-19 patients being administered remdesivir in a large, multi-center, clinical trial led by the NIAID. The scientists posted the work (link is external) on the preprint server bioRxiv.
The findings are not yet peer-reviewed and should not be considered clinical advice, but are being shared to assist the public health response to COVID-19. A study detailing the development of the rhesus macaque model of mild- to-moderate human disease, conducted by the same team of NIAID scientists, was posted to bioRxiv (link is external) on March 21.
The current study of remdesivir, a drug developed by Gilead Sciences Inc. and NIAID-supported investigators, involved two groups of six rhesus macaques. One group of monkeys received remdesivir and the other animals served as an untreated comparison group. Scientists infected both groups with SARS-CoV-2.
Twelve hours later the treatment group received a dose of remdesivir intravenously, and then received a daily intravenous booster dose thereafter for the next six days. The scientists timed the initial treatment to occur shortly before the virus reached its highest level in the animals’ lungs.
Twelve hours after the initial treatment, the scientists examined all animals and found the six treated animals in significantly better health than the untreated group, a trend that continued during the seven-day study.
They report that one of the six treated animals showed mild breathing difficulty, whereas all six of the untreated animals showed rapid and difficult breathing. The amount of virus found in the lungs was significantly lower in the treatment group compared to the untreated group, and SARS-CoV-2 caused less damage to the lungs in treated animals than in untreated animals.
The investigators note that the data supports initiating remdesivir treatment in COVID-19 patients as early as possible to achieve maximum treatment effect. The authors, from NIAID’s Rocky Mountain Laboratories in Hamilton, Montana, also note that while remdesivir helped prevent pneumonia, it did not reduce virus shedding by the animals. “This finding is of great significance for patient management, where a clinical improvement should not be interpreted as a lack of infectiousness,” they write.
NIAID conducts and supports research — at NIH, throughout the United States, and worldwide — to study the causes of infectious and immune-mediated diseases, and to develop better means of preventing, diagnosing and treating these illnesses. News releases, fact sheets and other NIAID-related materials are available on the NIAID website.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation’s medical research agency, includes 27 institutes and centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit www.nih.gov.